Clean Energy
The people of today still rely on burning fossil fuels to generate energy. This process is not energy efficient and is a great contributor towards possible catastrophic events due to climate change. The dependence on fossil fuels results to its depletion which also leads to increase in economic costs due to limited supply. Thus, it is necessary for us to find alternative modes of energy generation. Inasmuch as energy generation is of primary concern, energy storage can also be very essential to aid in efficient usage of energy. Fuel cells, which is one of few alternative means of energy generation, can also act as a tool to store energy. Utilization of electrochemical reactions whose species has virtually no environmental impacts can aid in achieving an ideal, sustainable means of generating and storing energy.
Water splitting reaction (Scheme) is at the forefront of clean energy sources. However, conventional electrodes utilizes costly electrocatalysts, such as Ru, Ir and Pt, to sustain reactions. Utilization of affordable catalysts using oxides and oxyhydroxides of earth-abundant transition metals as electrocatalysts are promising alternatives towards efficient water-based electrocatalytic reactions. Our research focuses producing metal oxide- or oxyhydroxide-based nanocomposites that could be able to achieve efficiency towards oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Rational design of such materials could possibly help us understand the possible mechanisms that could interplay within such reactions which still baffled many research groups up until today. Currently, our research is focused on utilizing thin films and graphene-metal oxide nanocomposites.
Thin films
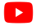
We have discovered the aid of yielding efficient hydrogen peroxide oxidation reactions using multivalent ions within cobalt-manganese oxyhydroxide (CMOH). We have transcended this concept towards OER applications through using a facile process to deposit CMOH on different electrode substrates by using potassium permanganate as precursor. OER activity can still be achieved across each substrates which reflects the versatility of the method. [1] (This work was featured in the inside front cover of J. Mater. Chem. A., Figure 1) Current understanding and application of this deposition technique on other substrates is still underway.
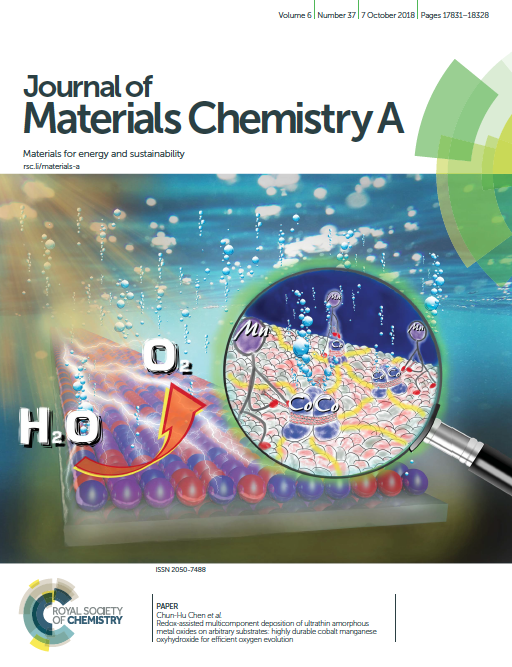
Fig. 1. Facile CMOH thin-film deposition featured at the inside front cover of Journal of Materials Chemistry A [1]
Graphene-metal oxide nanocomposites
Utilization of the electronic activities of graphene oxide has been realized to help in enhancement of certain electrocatalytic reactions. Electrocatalysts containing metal-nitrogen-carbon moieties were gaining attention due to their efficient ORR activity. We afforded a procedure which allows simultaneous formation of metal oxide-graphene nanocomposites and N-doping of graphene oxide. We have discovered the solvent dependence of the method, as utilization of dimethylformamide (DMF) facilitates the replacement of oxygen moieties within graphene with nitrogen as it simultaneously coordinates with the metal (Figure 2). Yielding such nanocomposite in DMF yielded a much lower ORR potential than preparing it using other solvents. [2]
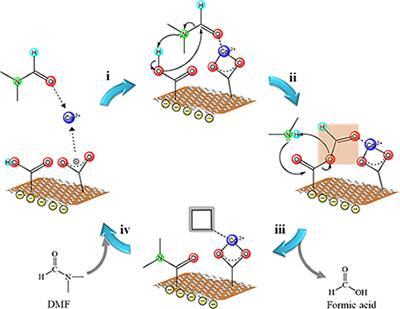
Fig. 2. Proposed mechanism for the solvent-dependence on the formation of metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite [2]
We have also achieved silver-hematite heterojunctions on graphene which leads to enhance ORR properties under laser irradiation, dubbed as laser-coupled ORR (LORR, Figure 3). [3] (This work was featured at the inside back cover of Chem. Commun.) Understanding the enhancement mechanisms is currently under study.
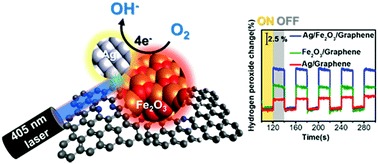
Fig. 3. Initial findings for LORR properties within silver-hematite heterojunctions were reported at Chemical Communications which was featured at the back cover. [3]
References/Related Works:
[1] Jhang, R.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Shih, M.-C.; Ho, J.-Q.; Tsai, Y.-T. ; Chen, C.-H.* Redox-assisted Multicomponent Deposition of Ultrathin Amorphous Metal Oxides on Arbitrary Substrates: Highly Durable Cobalt Manganese Oxyhydroxide for Efficient Oxygen Evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6, 17915 (2018)
[2] Kao, W.-Y.; Chen, W.-Q.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Ho; Y.-H.; Chen, C.-H.* General Solvent-dependent Strategy toward Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Graphene/Metal Oxide Nanohybrids: Effects of Nitrogen-containing Solvent. Sci. Rep. 6, 37174 (2016)
[3] Chen, W.-Q.; Chung, M.-C.; Valinton, J. A. A.; Penaloza Jr, D.P.; Chuang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-H.* Heterojunctions of Silver–iron Oxide on Graphene for Laser-coupled Oxygen Reduction Reactions. Chem. Commun. 54, 7900 (2018)